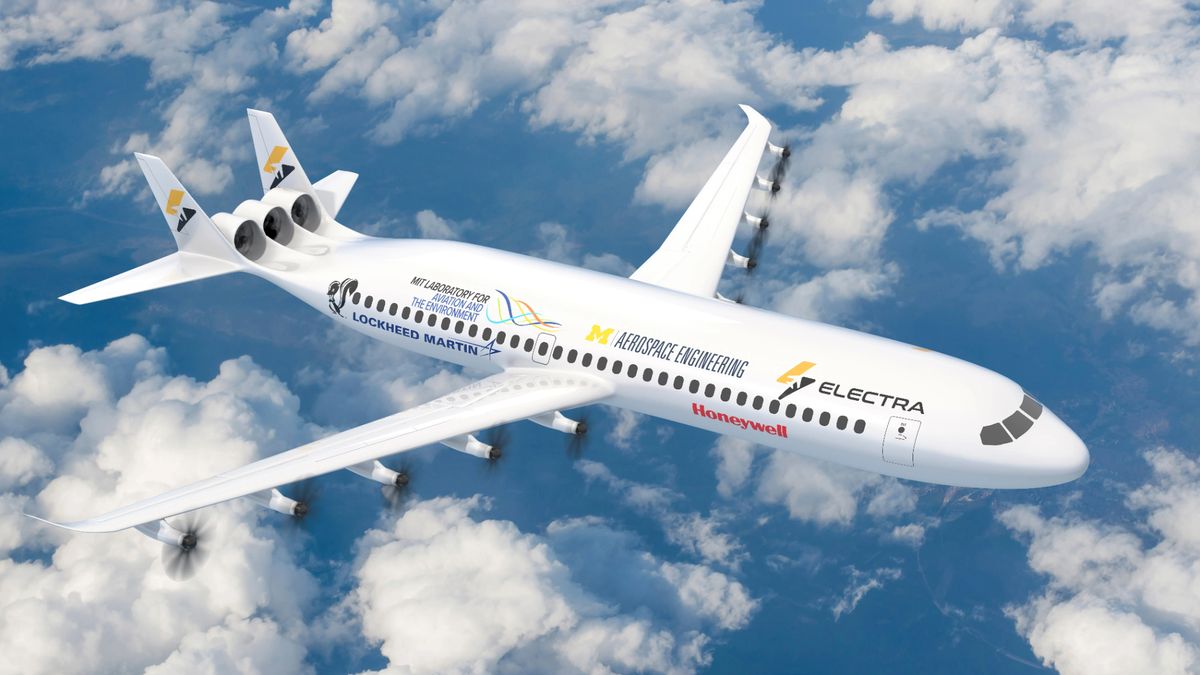
NASA is looking to develop a new generation of low-emission commercial aircraft that will offer a more efficient and sustainable mode of travel.
The space agency has commissioned five new design studies as part of its Advanced Aircraft Concepts for Environmental Sustainability (AACES) 2050 initiative. The organizations contributing to new airliner design concepts include Boeing’s Aurora Flight Sciences, the aerospace company Electra, the Georgia Institute of Technology, the aviation startup JetZero and Pratt & Whitney, according to a statement from NASA.
“Through initiatives like AACES, NASA is positioned to harness a broad set of perspectives about how to further increase aircraft efficiency, reduce aviation’s environmental impact and enhance U.S. technological competitiveness in the 2040s, 2050s and beyond,” Bob Pearce, NASA associate administrator for the Aeronautics Research Mission Directorate, said in the statement.
Awards issued to support the five NASA-funded studies total $11.5 million. Each organization brings unique expertise to designing a next-generation aircraft concept, ranging from alternative fuel sources to propulsion technologies and aerodynamic vehicle design.
You may like
Related: Airplane contrails are a tricky, and surprising, contributor to global warming
“As a leader in U.S. sustainable aviation research and development, these awards are one example of how we bring together the best ideas and most innovative concepts from the private sector, academia, research agencies and other stakeholders to pioneer the future of aviation,” Pearce said in the statement.
Aurora Flight Sciences’ area of study will examine alternative aviation fuels, propulsion systems, aerodynamic technologies and aircraft configurations. The Electra-led team will explore electric propulsion as well as unique aerodynamic design features for the aircraft’s main body and wings that will help reduce both emissions and noise.
Georgia Institute of Technology researchers will focus on sustainability technologies, including alternative fuels, propulsion systems, and aircraft configurations, while JetZero will explore technologies that enable cryogenic liquid hydrogen to be used as a fuel source to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Pratt & Whitney’s area of study will include aviation propulsion technologies, focusing on thermal and propulsive efficiency improvements to reduce fuel consumption and greenhouse gas emissions that contribute to global warming.
RELATED STORIES:
“The proposals selected come from a diverse set of organizations that will provide exciting and wide-ranging explorations of the scenarios, technologies, and aircraft concepts that will advance aviation towards its transformative sustainability goals,” Nateri Madavan, director for NASA’s Advanced Air Vehicles Program, which AACES falls under, said in the statement.
The aircraft design concepts developed through AACES could enter service within the next 25 years. By making aircraft less dependent on traditional fuel sources that contribute to greenhouse gas emissions, NASA is helping to support the U.S. goal of net-zero aviation emissions by 2050. You can find additional details for each of five NASA-funded studies here.